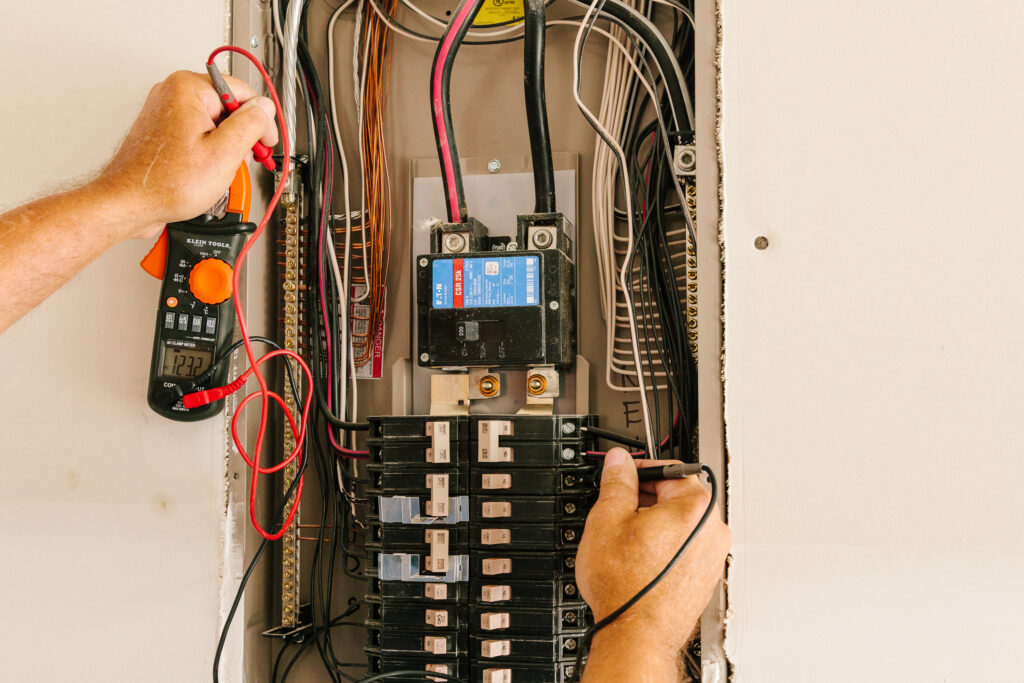
Balancing loads in a commercial electrical panel is essential for ensuring efficiency, safety, and longevity of the electrical system. An imbalanced load can lead to overheating, power fluctuations, increased energy costs, and potential damage to electrical equipment. Proper load balancing helps distribute power evenly across circuits, preventing excessive strain on one phase while underutilizing another. This guide explains how commercial electricians properly balance loads in a commercial electrical panel to maintain optimal performance and prevent operational disruptions.
Understanding Load Balancing
Load balancing refers to distributing electrical loads evenly across all phases in a commercial electrical panel. In a three-phase system, this means ensuring that each phase carries an approximately equal amount of current. When loads are balanced, electrical systems operate efficiently, reducing the risk of voltage drops, overheating, and unnecessary wear on transformers and circuit breakers.
Importance of Load Balancing
- Prevents Overloading: Unequal distribution of power can overload certain circuits, leading to circuit breaker trips and potential electrical fires.
- Enhances Energy Efficiency: A well-balanced system reduces energy waste and lowers operational costs.
- Extends Equipment Lifespan: Reducing stress on electrical components improves their longevity and decreases the need for costly repairs.
- Minimizes Voltage Fluctuations: Consistent voltage across all phases ensures reliable operation of machinery and other electrical devices.
Steps to Properly Balance Loads in a Commercial Electrical Panel
Step 1: Perform a Load Analysis
Commercial electricians begin by analyzing the current load distribution. This process includes:
- Measuring Load Current: Using a clamp meter or power quality analyzer, electricians measure the current on each phase.
- Identifying Imbalances: A difference of more than 10-15% between phases indicates a significant imbalance that needs correction.
- Evaluating Peak Loads: Examining power usage during peak operational hours helps identify circuits that may need redistribution.
Step 2: Identify and Categorize Loads
To effectively balance loads, electricians categorize the electrical devices connected to the panel:
- Resistive Loads: Equipment such as heaters and incandescent lights that draw a constant current.
- Inductive Loads: Motors, compressors, and HVAC systems that may cause phase imbalances due to their starting currents.
- Electronic Loads: Computers, LED lighting, and office equipment, which can introduce harmonic distortions.
Categorizing loads allows for strategic redistribution, ensuring that similar types of loads are spread evenly across phases.
Step 3: Reallocate Circuit Breakers
If an imbalance is detected, commercial electricians will redistribute circuit breakers to balance the load. This involves:
- Switching High-Power Loads: Moving circuits with high current draw to a less loaded phase.
- Alternating Load Distribution: Ensuring that high-draw equipment is spread across all three phases instead of being concentrated on one.
- Balancing Single-Phase Loads: Distributing single-phase loads evenly across different phases in a three-phase system.
Step 4: Monitor Voltage and Current Levels
After redistributing loads, commercial electricians measure voltage and current levels again to confirm the improvement. They ensure:
- Each phase carries a similar current load.
- Voltage across all phases remains within acceptable limits.
- No single circuit is overloaded or underloaded.
Step 5: Implement Load Management Strategies
To maintain a balanced electrical panel, businesses can implement the following strategies:
- Scheduling High-Power Equipment Usage: Avoiding simultaneous operation of high-draw equipment during peak hours.
- Using Automatic Load Balancing Systems: Some modern electrical panels feature smart load-balancing systems that automatically adjust circuits.
- Installing Phase Monitors: These devices alert facility managers when phase imbalances occur, allowing for timely corrective actions.
Common Challenges in Load Balancing and How to Overcome Them
1. Unequal Equipment Distribution
- Solution: Ensure similar types of equipment are spread evenly across circuits instead of clustering high-power loads on one phase.
2. Unexpected Load Changes
- Solution: Conduct periodic load analyses to accommodate business growth and equipment upgrades.
3. Voltage Drops Due to Long Circuit Runs
- Solution: Use appropriately sized conductors to minimize resistance and voltage loss over long distances.
4. Harmonic Distortions Affecting Balance
- Solution: Install harmonic filters and use power factor correction devices to stabilize electrical loads.
Regular Maintenance for Load Balancing
Commercial electricians recommend routine maintenance to keep loads balanced and prevent future issues:
- Quarterly Load Testing: Measuring loads at different times of the day to identify potential imbalances.
- Breaker Inspection: Checking for loose or overheating breakers that could indicate load distribution problems.
- Voltage and Current Monitoring: Using digital monitoring tools to track load distribution trends over time.
Conclusion
Proper load balancing in a commercial electrical panel ensures electrical efficiency, enhances equipment lifespan, and reduces safety risks. Commercial electricians play a crucial role in analyzing, redistributing, and maintaining balanced loads to prevent operational disruptions. By following systematic load-balancing procedures, monitoring voltage levels, and implementing load management strategies, businesses can optimize their electrical systems for long-term performance and reliability.
Stay in touch to get more news & updates on Internet Chicks!